Most people aspire to enhance their physical fitness and overall well-being, but few understand the comprehensive benefits of a dedicated strength and conditioning program. As you launch on this journey, you’ll discover how tailored workouts can lead to increased muscle strength, improved endurance, and enhanced athletic performance. This post will guide you through the crucial components of strength and conditioning, emphasizing key strategies that can help reduce injury risk while building a stronger, more resilient you. Embrace the challenge, and take the first step towards your fitness goals today!
Key Takeaways:
- Implement a tailored strength training program that addresses individual goals and fitness levels for effective results.
- Incorporate a balanced approach of strength, flexibility, and endurance exercises to achieve overall physical development.
- Prioritize proper nutrition and recovery techniques to enhance performance and support muscle growth.
The Core Principles of Strength and Conditioning
The foundation of strength and conditioning lies in understanding the principles that guide effective training. These core principles include specificity, progression, overload, and variation. By focusing on these fundamental aspects, you can design a program that targets your unique goals while ensuring continuous improvement. This structured approach enables you to build strength, enhance endurance, and optimize overall performance, laying the groundwork for long-term fitness success.
The Science of Muscle Adaptation
Muscle adaptation is a fascinating process that occurs as you train. When you introduce stress to your muscles through resistance exercises, your body responds by enhancing its strength and endurance capabilities. This is achieved through physiological changes, such as increased muscle fiber size and improved neural recruitment. Over time, these adaptations allow you to lift heavier weights and perform more complex movements, ultimately leading to a stronger physique.
The Role of Energy Systems in Performance
Your body relies on three primary energy systems to fuel its activities: the phosphagen system, glycolytic system, and oxidative system. Each of these systems contributes to various exercise intensities and durations, impacting your overall performance. Understanding how these energy systems function empowers you to tailor your training regimen effectively.
The phosphagen system provides immediate energy for high-intensity bursts, lasting about 10 seconds, making it ideal for activities like sprinting or heavy lifting. In contrast, the glycolytic system kicks in during moderate to high-intensity efforts, lasting up to 2 minutes, useful for activities such as repeated sprints. Finally, the oxidative system supports lower-intensity, sustained efforts, primarily during long-duration activities like distance running or cycling. By strategically training each energy system, you can enhance both your anaerobic and aerobic capacities, leading to improved performance across a variety of athletic pursuits.
Breaking Down Effective Training Programs
Effective training programs are tailored to your specific goals, incorporating both strength and conditioning elements for comprehensive fitness. An ideal program should include a mix of weightlifting, resistance training, and cardiovascular exercises, allowing you to progressively challenge yourself and avoid plateaus. By assessing your fitness level and desired outcomes, you can create a program that not only fits your lifestyle but also keeps you engaged and motivated throughout your journey.
Strength Training Techniques: From Weights to Bodyweight
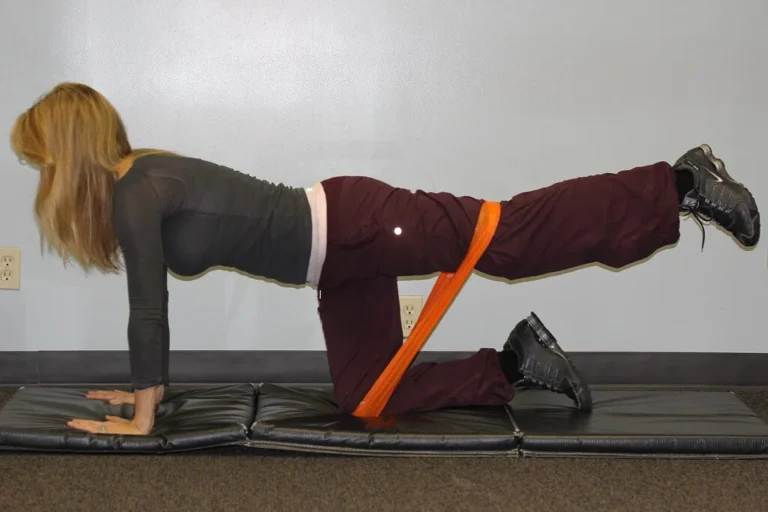
Strength training employs diverse techniques that range from traditional weights to innovative bodyweight exercises. Utilizing free weights, resistance bands, or machines can enhance muscular growth, while bodyweight movements like push-ups, squats, and lunges improve strength and stability. Combining various methods helps to challenge your muscles in different ways, promoting overall strength and functional fitness.
Conditioning Strategies: HIIT vs. Steady-State Cardiovascular Training
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) and steady-state cardiovascular training are two distinct approaches that offer unique benefits. HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by recovery periods, making it time-efficient and highly effective for fat loss. On the other hand, steady-state cardio, such as jogging or cycling at a consistent pace, helps improve endurance and cardiovascular health over longer periods. Balancing both methods in your routine can maximize fitness outcomes.
Comparing HIIT and steady-state training reveals significant differences in cardiovascular responses and caloric expenditure. HIIT workouts can burn up to 30% more calories in a shorter time frame due to the afterburn effect, which keeps your metabolism elevated post-exercise. This makes HIIT particularly appealing for those with limited time. Conversely, steady-state cardio is excellent for building endurance and can be maintained for longer durations, making it highly suitable for long-distance preparations. A strategic balance of both methods not only keeps your workouts varied but also optimally targets your fitness goals, aiding in both strength and conditioning development.
The Importance of Nutrition in Strength and Conditioning
Nutrition serves as the foundation for all strength and conditioning efforts, as the right fuels and nutrients help set the stage for optimal performance and recovery. A well-planned diet not only enhances your physical capabilities but also aids in muscle repair, growth, and hormonal balance. Incorporating vital macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—will ensure you are equipped to meet the demands of your training regimen, while a focus on micronutrients promotes overall health and energy levels.
Nutritional Strategies to Support Muscle Growth
To maximize muscle growth, you need to integrate a balanced intake of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats into your diet. Aim for at least 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to stimulate muscle protein synthesis effectively. Combining this with complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, provides the energy needed for intense training sessions. Timing your meals—particularly focusing on protein intake post-workout—can further enhance recovery and muscle-building efforts.
Hydration and Recovery: Optimizing Performance
Hydration plays a vital role in both performance and recovery during strength training. Water is vital for regulating body temperature and maintaining electrolyte balance, while dehydration can significantly hinder your strength and endurance. Aim for at least half your body weight in ounces daily and increase intake during intense workouts or hotter climates. Electrolyte-replenishing beverages may also be beneficial after strenuous exercise, helping restore balance and accelerate recovery.
Inadequate hydration levels can result in diminished strength, increased perceived exertion, and longer recovery times. Studies suggest that even a 2% drop in body weight due to fluid loss can impair performance. Prioritizing hydration throughout the day—not just during workouts—ensures that your muscles remain nourished and responsive, improving your overall training experience. Listen to your body and drink regularly to keep fluids topped up, and consider incorporating electrolyte-rich drinks during prolonged or intense exercise sessions.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Many individuals initiateing on strength and conditioning journeys fall victim to common pitfalls that can hinder progress and lead to injury. By recognizing these issues early, you can adjust your approach and create a more effective training regimen. Avoiding overtraining, dismissing recovery, and buying into myths like “no pain, no gain” are just a few hurdles you may encounter. Identifying and addressing these challenges will help you maximize your potential while safeguarding your health.
Overtraining: Recognizing and Responding
Overtraining occurs when you push your body beyond its limits without allowing adequate recovery time, leading to fatigue, decreased performance, and increased injury risk. Signs include persistent soreness, irritability, and disrupted sleep patterns. If you experience these symptoms, it’s vital to adjust your training schedule by incorporating rest days or reducing workout intensity. Listening to your body is key; prioritize recovery to ensure long-term gains and performance improvements.
The Myth of ‘No Pain, No Gain’
The saying “no pain, no gain” can be misleading and may lead you to believe that discomfort is a necessary part of progress. While it’s natural to feel some level of exertion during workouts, pain can indicate injury rather than growth. It’s crucial to differentiate between healthy fatigue and harmful pain. Prioritize recovery and modify your training regimen to include appropriate rest periods, ensuring your body has time to adapt and strengthen.
In reality, pain should never be equated with gain. The notion that you must suffer to achieve results can lead to poor fitness choices, including pushing through injury or ignoring signs of overtraining. Instead, focus on sustainable training practices that promote gradual progress while respecting your body’s limits. Implementing a balanced routine, integrating rest days, and using proper techniques will help you avoid injury and encourage long-lasting results, making fitness a rewarding part of your lifestyle.
Psychological Strategies to Enhance Performance
Incorporating psychological strategies into your training can significantly boost your performance. Techniques like visualizing success, practicing mindfulness, and maintaining a positive self-talk routine can foster an enhanced mental state. Using these strategies, you can unlock your potential, allowing for a more focused and productive training session, ultimately translating into better physical results.
The Power of Goal Setting: SMART Goals for Success
Implementing SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—can elevate your training regimen. For instance, rather than aiming to “get stronger,” commit to “increasing your squat by 20 pounds in the next three months.” This clarity keeps you motivated and on track, enhancing your overall commitment to your strength and conditioning objectives.
Mental Resilience: Building a Strong Mindset
Developing mental resilience is a key component of achieving lasting success in strength and conditioning. By learning to embrace challenges and setbacks as opportunities for growth, your confidence in facing tough workouts will rise. This resilience not only improves your performance during training but also solidifies your commitment to your fitness journey, helping you push through tough times.
Fostering mental resilience involves more than just optimism; it’s about cultivating a growth mindset. Engaging in regular self-reflection allows you to assess your challenges and set a plan to overcome them. Effective strategies like journaling your performance, visualizing your success before workouts, or practicing deep-breathing techniques can help create a strong mental foundation. Notably, studies show that athletes who focus on building resilience often report increased satisfaction in their training and better results, reinforcing the notion that a strong mind is a powerful ally in your quest for strength.
Summing up
Now that you understand the importance of strength and conditioning, you have the tools to build a stronger version of yourself. By integrating targeted exercises and proper nutrition into your routine, you can enhance your performance, increase your resilience, and improve your overall well-being. Take the initiative to design a personalized program that suits your unique goals and lifestyle. Embrace the journey of self-improvement and watch as your hard work translate into lasting strength and confidence.
FAQ
Q: What is Strength and Conditioning and how does it benefit me?
A: Strength and Conditioning is a specialized fitness regimen designed to enhance overall athletic performance and physical health. It involves combining strength training, endurance exercises, mobility work, and conditioning drills tailored to individual needs and goals. Key benefits include improved muscular strength, increased endurance, better flexibility, and enhanced overall physical performance, leading to a healthier lifestyle and reduced risk of injury.
Q: How often should I engage in Strength and Conditioning workouts?
A: The frequency of Strength and Conditioning sessions can vary based on personal fitness levels, goals, and training experience. Generally, it’s advisable to aim for at least 2-3 sessions per week. These workouts can be adjusted over time to include more advanced techniques, depending on progress. It’s also important to allow adequate recovery time between sessions to prevent fatigue and potential injuries.
Q: What equipment do I need for a Strength and Conditioning program?
A: Equipment requirements can be minimal or extensive, depending on the specific program and goals. Basic equipment for a Strength and Conditioning regimen might include free weights (dumbbells and kettlebells), resistance bands, a stability ball, and a mat for floor exercises. For those looking for more advanced options, gym machines, barbells, and jump ropes can also be included. Ultimately, the best approach is to select equipment that aligns with your objectives and preferences.